Call
+212 0522274820+212 0522276640
+212 661134182
 Medic Interface Maroc
Medic Interface Maroc
 Medic Interface Maroc
Medic Interface Maroc
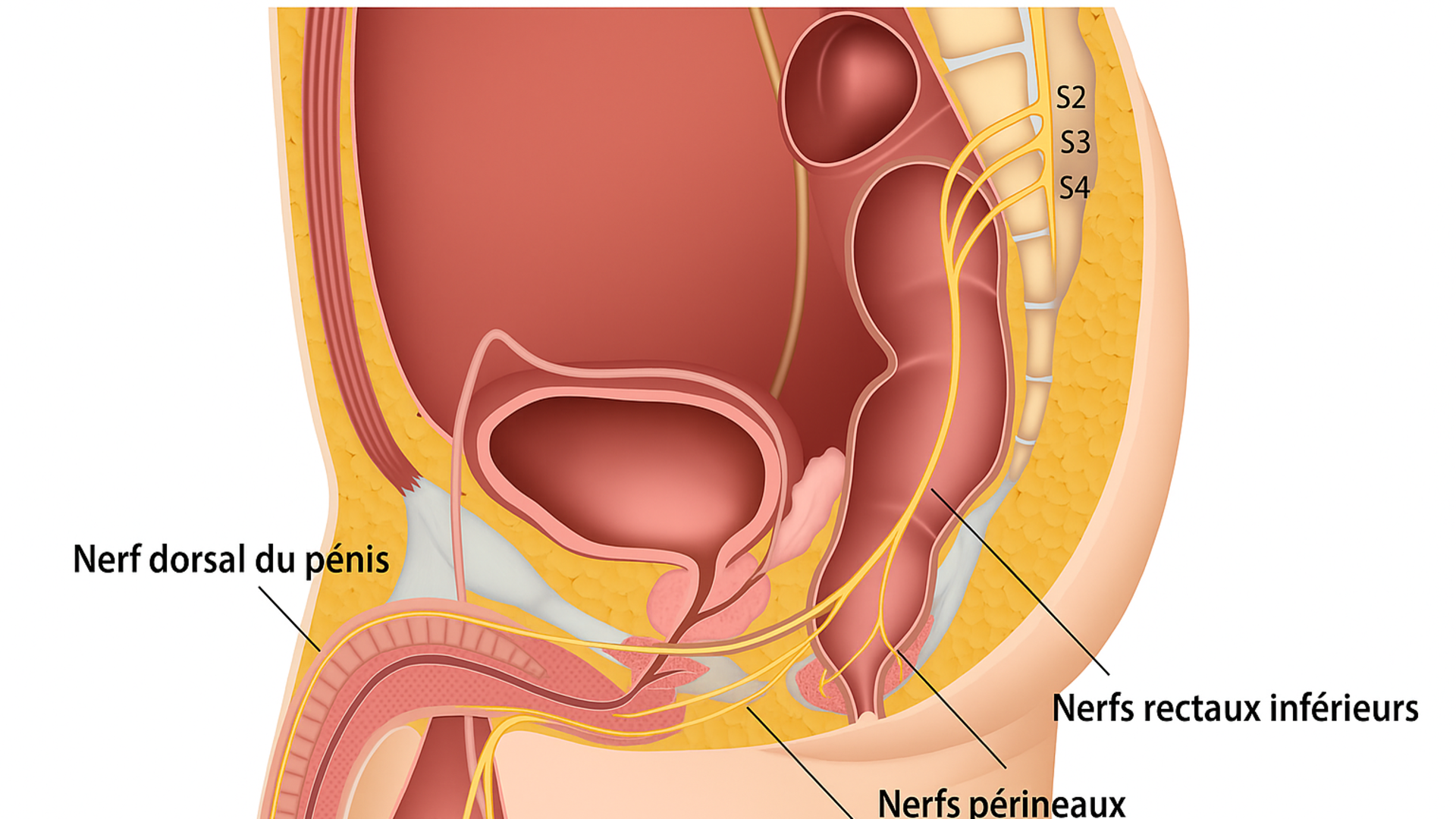
This is a painful perineal condition that generally occurs from the age of forty, with a female predominance (2/3 of cases).
However, it often does not spare people around the age of 30.
The pudendal nerve is a sensory and motor autonomic nerve.
It exits the spinal cord in the lowest region (perineum).
This nerve dominates and 'governs' the perineum.
It has a necessary passage that runs along the lesser pelvis, inserts between two ligaments:
the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament, and then enters a fibrous canal (Alcock's canal). It then gives off three branches: the perineal nerve, the dorsal nerve of the penis in men or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris in women, and the inferior rectal nerve.
This nerve can be constricted in its path, and it will suffer from this constriction. The division branches that originate from it also suffer, as do the organs and muscles they innervate.
This is what constitutes pudendal neuralgia, characterized by pain extending from the pubis to the anus. Its diagnosis is eminently clinical, and all tests performed are normal. The pain is exacerbated when sitting and relieved when lying down. It resembles a burning sensation caused by discharges or gravity, with a sensation of an intravaginal or intrarectal foreign body. Triggered by the clinical examination, which, upon vaginal and/or rectal examination, will cause identical pain. Proof of diagnosis can be provided by a block test, which consists of an ultrasound-guided or, better still, CT-guided injection of an anesthetic, with or without a corticosteroid. The result is immediate. This pathology is little known among physicians, leading to diagnostic inaccuracy and psychiatric treatment of the disease, resulting in delayed diagnosis.
Several treatments are available: medical, physiotherapy, chiropractic, radiofrequency, cryo-neurolysis, all with a transient effect, more of a placebo effect.
But the most effective are:
Medical treatment adapted to each case and well conducted.
Phone
+212 0522274820
+212 0522276640
+212 661134182
contact@medicinterfacemaroc.com
Address
12, Boulevard d'Anfa, Casaclanca - Maroc
© Medic Interface Maroc. All rights reserved.
Designed by modiom Tech
